Describe the Structure of the Cytoskeleton.
It also helps to facilitate communication among intracellular organelles. It helps transport inside the cytoplasm like the movement of vesicles and organelles for example and it helps in.

The Cytoskeleton Flagella And Cilia And The Plasma Membrane Biology For Non Majors I
In animal cells the exterior side of the plasma membrane is in contact with the extracellular environment.

. The cytoskeleton is a kind of temporary structure present in all the cells within any living organism. Overview of Structure Of Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers like protein filaments spread throughout the cytoplasm except for the nucleus. Elucidate the general mechanism by which molecular motors move along cytoskeletal elements.
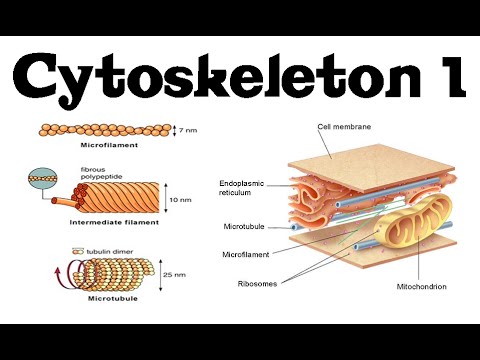
Identify the molecular motors dyneins kinesins and myosins that partner with various cytoskeletal elements. Microfilaments are three to six nanometers in diameter and are composed of the protein. It is a complex dynamic biopolymer network comprising microtubules actin and intermediate filaments.
Structure of Cytoskeleton Definition The cytoskeleton is a mesh of filaments and tubules made up of protein continued throughout the cytosol that is present in all types of cells. Microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Differ in size and each carries out specific functions within the cell.
Microfilaments are often associated with myosin. The cytoskeleton of most eukaryotic cells is composed of three basic structural components collectively called cytoskeletal elements. Intermediate filaments which serve to support the cell itself rapidly which.
Microtubules are hollow rods of the protein tubulin that interact with motor proteins to create movement within the cell. Collectively these fibers are termed as the cytoskeleton. The filaments that comprise the cytoskeleton are.
From narrowest to widest they are the microfilaments actin filaments intermediate filaments and microtubules. It provides rigidity and shape to the cell and enables cellular movements microtubule. A cellular structure like a skeleton contained within the cytoplasm.
The cytoskeleton is the major mechanical structure of the cell. Microfilaments intermediate filaments and microtubules Figure 1. From narrowest to widest they are the microfilaments actin filaments intermediate filaments and microtubules.
Cytoskeleton a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells cells containing a nucleus. It represents some fibrous proteins of the cytoplasm which help to maintain cell shape and give contractibility to the cell. Rapidly microtubules the cytoskeleton is made of three types of protein fibers.
Microfilaments The tiniest main component of the cytoskeleton is the microfilament. The term cytoskeleton refers to the cytoplasmic structures that provide mechanical support shape and strength to the cell in the same way that the human skeleton does for the human body. Like rubber bands they resist tension.
There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton structure is modified by adhesion to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix ECM. Both the individual filaments and the entire network are not simple elastic solids but are instead highly nonlinear structures.
Microtubules As their name implies microtubules are small hollow tubes. The cytoskeletal elements are composed of different proteins. Microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell.
Actin filaments microfilaments 3. The fibre of the cytoskeleton extends throughout the cell having interconnection with cell membrane and cell organelles. Appreciating the mechanics of biopolymer networks.
The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell through the cytoplasm which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements. This dynamic property enables cellular movement which is governed by forces both internal and external.
The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell maintains the cells shape and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles within it. Proteins form these structures which can be very small fibrous filamentous or tubular. Cytoskeleton as the name suggests is a skeletal system within the cytoplasm of a cell which consists of a variety of protein fibers that form a network and impart a certain shape and structure to the cell.
It is found in all cells though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. The cytoskeleton is made up of three major structures. The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and shape and allows them to move around.
In this outcome we will examine each. The cytoskeleton supports the cell gives it shape organizes and tethers the. Cytoskeletal component comprised of several fibrous protein intertwined strands that bears tension supports cell-cell junctions and anchors cells to extracellular structures microfilament the cytoskeleton systems narrowest element.
The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements. All three cell types have a plasma membrane that borders the cytoplasm on its interior side. Despite the rigidity implied by the term structure it is a dynamic complex that lends a certain amount of flexibility to the cell.
Microfilaments are often associated with myosin. The strength and the type of these adhesions are pivotal for regulating the assemblydisassembly of the cytoskeleton components. Cytoskeleton Definition The cytosol of cells contains fibers that help to maintain cell shape and mobility and that probably provide anchoring points for the other cellular structures.
Microtubules along with microfilaments and intermediate filaments come under the class of organelles known as the cytoskeleton. However in plant and bacteria cells a cell wall surrounds the outside of the plasma membrane. Types of cytoskeletal elements 1.
Distinguishing features of cytoskeletal elements 1. It is made of protein and it maintains the cell shape protects the cell and enables every cell to move freely using some specific structures such as flagella and cilia. Describe the traits and functions of the various cytoskeletal elements microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments.
In plants the cell wall is made of cellulose. They provide rigidity and shape to the cell and facilitate cellular movements. Microtubules intermediate filaments and microfilaments.
Often referred to as the bones and muscles of an animal cell the cytoskeleton functions in support such as vesicle transport of materials and movement determining a cells shape.
Cytoskeleton Structure And Function 1 Actin Microtubules And Intermediate Filaments Youtube

Cytoskeleton Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Cytoskeleton."
Post a Comment